Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, and its main goal is to understand how the universe behaves. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Physics
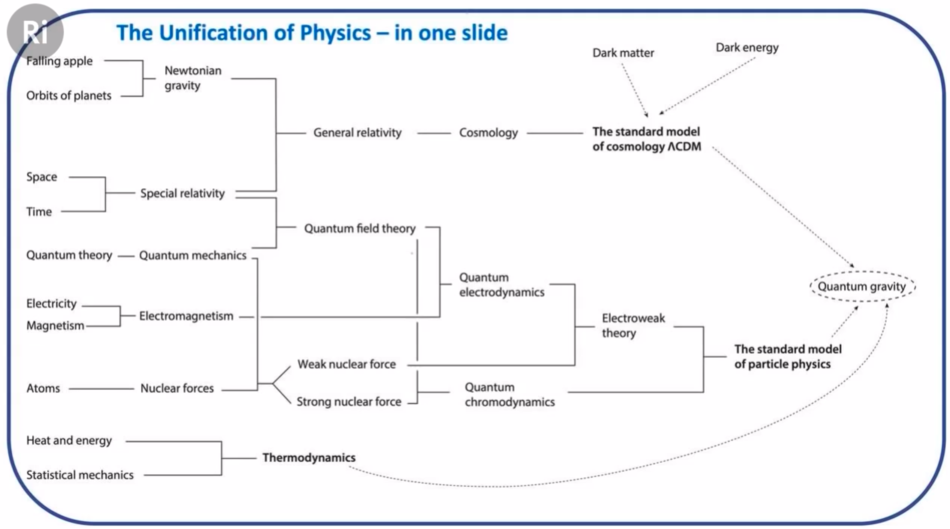
Contents
Signals
A signal is usually defined as:
- A signal is a function that represents the variation of a physical quantity with respect to any parameter (usually time or space) [with respect to at least one independent variable (time or space)]. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M0mx8S05v60 https://x-engineer.org/graduate-engineering/signals-systems/signal-processing/what-is-a-signal
- A signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Signal#Classification
In electronics, a signal is an electric current or electromagnetic field used to convey data from one place to another. The simplest form of signal is a direct current (DC) that is switched on and off; this is the principle by which the early telegraph worked. More complex signals consist of an alternating-current (AC) or electromagnetic carrier that contains one or more data streams. https://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/definition/signal
Sound, images and videos are also considered to be signals. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Signal#Classification
It is not clear if a signal must be a function of time/space; or if it can be of any other parameter.
It is neither clear if the signal is the physical phenomenon (for example, the seismic wave) or the functional representation of the physical phenomenon (the seismogram).
Signal analysis - Signal processing
One of the applications of Mathematical analysis (Calculus in particular) is for Signal processing. When processing signals, such as audio, radio waves, light waves, seismic waves, and even images, Fourier analysis can isolate individual components of a compound waveform, concentrating them for easier detection or removal. A large family of signal processing techniques consists of Fourier-transforming a signal, manipulating the Fourier-transformed data in a simple way, and reversing the transformation. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mathematical_analysis#Signal_processing
- Time-frequency analysis https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Time%E2%80%93frequency_analysis
- Fourier transform https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fourier_transform
- Seismic processing
- Time-frequency analysis in Seismic processing:
- A set of mathematical formulas used to convert a time function, such as a seismic trace, to a function in the frequency domain (Fourier analysis) and back (Fourier synthesis). The Fourier transform is used extensively in signal processing to design filters and remove coherent noise. Many filtering operations are performed in the frequency domain. The Fourier transform has applications in image analysis and in pattern recognition in geological systems. https://www.glossary.oilfield.slb.com/en/Terms/f/fourier_transform.aspx#:~:text=A%20set%20of%20mathematical%20formulas,and%20back%20(Fourier%20synthesis).&text=The%20Fourier%20transform%20is%20used,filters%20and%20remove%20coherent%20noise.
Relativity and the nature of time
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NrjFE_Rd2OQ
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-6rWqJhDv7M
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DPPnrDdNoUU
|
Theory of relativity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
1879 |
14 March |
Albert Einstein's birth 14 March 1879, Ulm, Kingdom of Württemberg, German Empire - 18 April 1955 (aged 76), Princeton, New Jersey, United States
|
The history of electricity
Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity -- Jim Al-Khalili BBC Horizon: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gtp51eZkwoI
The history of understanding the Atom
- Atom: Clash of Titans, Jim Al-Khalili: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GOJFznzSZhM https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CYQwrAhT7HA&list=RDCMUCZSE95RmyMUgJWmfra9Yx1A&index=2
- Ludwig Boltzmann 1844, Vienna, Austrian Empire -- 1906, Tybein, Triest, Austria-Hungary
One of the first to argue that mater is made of atoms.
- Albert Einstein 1879, Ulm, Germany - 1955 -- Princeton, New Jersey, U.S.
Brownian Motion https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i7tQLjGZR0A
Random Force & Brownian Motion - Sixty Symbols: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FAdxd2Iv-UA
Detailed explanation of Einstein's article on the Brownian motion: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4XI5pk7P-Yo
Brownian Motion is the random movement displayed by microscopic particles suspended in fluids. It was name after the botanist Robert Brown, who in 1827, performed experiments where he observed pollen seeds suspended in water under the microscope. The tiny grains suspended in water make random zigzag motions. This motion never appeared to slow o stop.
in 1905, Einstein developed a mathematical model for brownian motion based on atomos. Einstein explained that the pollen grains were being moved by water molecules around them. Einstein even derived how big atomos should be based on how the brownian particles move.
Einstein's model was the first hard evidence that supported the existence of atoms.
- Ernest Rutherford 1871, Brightwater, Colony of New Zealand -- 1937, Cambridge, England
In 1909, Rutherford performed an experiment in which This experiment
- Niels Bohr
...
- Quantum Jumps
...
- Schrdinger's wave equation
...
- Vener Heisenbeg: Uncertainty principle
...
|
The history of understanding the Atom |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fifth Solvay Conference | |
|
|
|
The Existence of Nothing
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1OLz6uUuMp8
The big bang theory
El físico teórico Brian Cox explica por qué el Big Bang sí ocurrió. He said, "you cannot claim there wasn't a big bang because you can fucking see it..." https://www.facebook.com/reel/529674369340908/?s=single_unit

