Multi-Paradigm Programming and Scripting
File:Some_important_programming_concepts.pdf
| Why Multi-Paradigm Programming and Scripting? | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Content of this course | |||
Programming Constructs:
|
Programming Paradigms & Languages:
|
Scripting:
|
Applications of Shell Scripting:
|
Contents
- 1 Some important programming concepts
- 1.1 High level - Low Level Programming
- 1.2 Compilation vs Interpretation
- 1.3 Procedural - Functional and Object-Oriented Programming
- 1.4 Languages evaluation criteria
- 1.5 Imperative versus declarative code
- 1.6 Names - Variables
- 1.7 Binding
- 1.8 Statically and Dynamically typed languages
- 1.9 Data type
- 1.10 Pointer
- 2 Object-Oriented Paradigm
- 3 Some tutorials
Some important programming concepts
High level - Low Level Programming
Compilation vs Interpretation
https://medium.com/@DHGorman/a-crash-course-in-interpreted-vs-compiled-languages-5531978930b6
https://guide.freecodecamp.org/computer-science/compiled-versus-interpreted-languages/
Speaking simplistically, compiled languages are those which are written in one language and, before being run, translated or "compiled" into another language, called the target language (typically in machine language that the processor can execute). Once the translation is complete, the executable code is either run or set aside to run later. Some common compiled languages include C, C++, Delphi and Rust.
The compiler translates the high-level source program into an equivalent target program (typically in machine language).
The alternative to using a compiler (for a compiled language) is using an interpreter (for interpreted languages). Interpreted languages are "interpreted" live in their original source code, although in reality they are merely compiled at runtime. What this allows for is a lot more flexibility, especially when it comes to a program adaptively modifying its structure. This flexibility does have a cost; interpreted languages are considered significantly slower.
Interpreters will run through a program line by line and execute each command.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Compiled Languages:
- Advantages:
- Programs compiled into native code usually tend to be faster than those translated at run time, due to the overhead of the translation process.
- Disadvantages:
- The compile code usually Platform dependence of the generated binary code.
Interpreted Languages:
- Advantages:
- Greater flexibility
- Better diagnostics (error messages)
- An Interpreted language gives implementations some additional flexibility over compiled implementations. Because interpreters execute the source program code themselves, the code itself is platform independent (Java's byte code, for example). Other features include dynamic typing, and smaller executable program size.
- Disadvantages:
- The most notable disadvantage is typical execution speed compared to compiled languages.
- Interpreted languages were once known to be significantly slower than compiled languages. But, with the development of just-in-time compilation, that gap is shrinking.
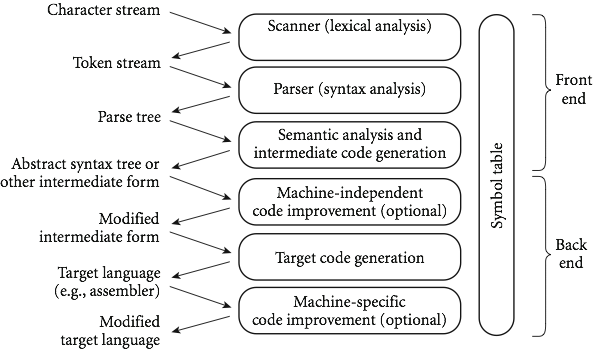
Phases of Compilation
- Scanning:
- Parsing:
- Semantic analysis:
- Intermediate form :
- Optimization:
- Code generation phase :
Procedural - Functional and Object-Oriented Programming
Can we do Object-Oriented Programming with ANSI-C? Yes! this book explains how to do it: https://www.cs.rit.edu/~ats/books/ooc.pdf
https://www.codecademy.com/articles/cpp-object-oriented-programming
https://owlcation.com/stem/Use-Of-Object-Oriented-Programming
https://searchapparchitecture.techtarget.com/definition/object-oriented-programming-OOP
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/object-oriented-programming-oops-concept-in-java/
http://ee402.eeng.dcu.ie/introduction/chapter-1---introduction-to-object-oriented-programming
Subprogram - Procedure - Function - Method - etc
Subprograms
Subprograms are the fundamental building blocks of programs and are therefore among the most important concepts in the programming language design.
- Subprogram header is the fist part of the definition including the name, the kind of subprogram, and the formal parameters.
- The parameter profile (aka signature) of a subprogram is the
number,orderandtypesof its parameters. - The protocol is a subprogram parameter profile and, if it is a function, its return type.
There are tow categories of subprograms:
- Procedures: are collection of statements that define parameterized computations.
- Functions: structurally resemble procedures but are semantically modeled on mathematical functions.
Design issues for Subprograms:
- Are local variables static or dynamic?
- What types of values can be returned from functions?
- How many values can be returned from functions?
- Can subprograms be overloaded?
- Can subprogram be generic?
- Is the language allowed nested subprograms?
Some important concepts around Subprograms are:
- Parameter-passing:
- Pass-by-Value (In Mode)
- Pass-by-Result (Out Mode)
- Pass-by-Reference (Inout Mode)
- Local referencing environments
- Generic subprograms
- Overloaded subprograms
Generic subprograms
A generic subprogram is one that takes parameters of different types on different activation.
Following example illustrates how we can print an array of different type using a single Generic method: https://www.tutorialspoint.com/java/java_generics.htm
public class GenericMethodTest {
// generic method printArray
public static < E > void printArray( E[] inputArray ) {
// Display array elements
for(E element : inputArray) {
System.out.printf("%s ", element);
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Create arrays of Integer, Double and Character
Integer[] intArray = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
Double[] doubleArray = { 1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4 };
Character[] charArray = { 'H', 'E', 'L', 'L', 'O' };
System.out.println("Array integerArray contains:");
printArray(intArray); // pass an Integer array
System.out.println("\nArray doubleArray contains:");
printArray(doubleArray); // pass a Double array
System.out.println("\nArray characterArray contains:");
printArray(charArray); // pass a Character array
}
}
Overloaded subprograms
An overloaded subprogram is one that has the same name as another subprogram in the same referencing environment. However, every version of an overloaded subprogram has a unique protocol.
C++, Java, C#, and Ada include predefined overloaded subprograms. They allow users to write multiple versions of subprograms with the same name and different protocols. In Ada, the return type of an overloaded function can be used to disambiguate calls (thus two overloaded functions can have the same parameters)
Recursion
https://www.python-course.eu/recursive_functions.php
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/recursion/
The process in which a function calls itself directly or indirectly is called recursion and the corresponding function is called as recursive function. Using recursive algorithm, certain problems can be solved quite easily. Examples of such problems are Towers of Hanoi (TOH), Inorder/Preorder/Postorder Tree Traversals, DFS of Graph, etc.
A VERY VERY NICE example of recursion is the factorial function:
Example:
4! = 4 * 3!
3! = 3 * 2!
2! = 2 * 1
Replacing the calculated values gives us the following expression
4! = 4 * 3 * 2 * 1
def factorial(n):
if n == 1:
return 1
else:
return n * factorial(n-1)
Object-oriented programming
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming language paradigm structured around objects (which consists of both data and behaviors[Functions-Methods]). This is in contrast to conventional Functional programming paradigm that is structured based on actions (logic) and only loosely connects data and behaviors.
A traditional functional/procedural(*) program is structured based on actions (logic). In general, a functional program take an input data, process it and produces a result. In other words, the data, stored in variables, is passed to defined functions which perform some action and modify it or create new data. The program is centralized around the actions (logic):
- Take input data
- Process the data
- Produces a result
The object-oriented paradigm allows us to structure the program as a collection of objects that consist of both data and behaviors[Functions-Methods]. So, in object-oriented programming, data and functions are tied together in an entity called object. We can said that one of the main aim of OOP is to bind together the data and the functions that operate on them so that no other part of the code can access this data except that function. These data in OOPs are known as properties and functions used to modify properties are called methods.
The object-oriented programming approach encourages:
- Modularisation: where the application can be decomposed into modules.
- Software re-use: where an application can be composed from existing and new modules.
Major benefits of using OOPs:
- Encapsulation : Objects created in OOPs are able to hide certain parts of code from programmer. This prevents unintentional modification in the code which may cause unwanted outcomes.
- Code Reuse : Objects created in OOPs can easily be reused in other programs.
- Software Maintenance : Code written in OOPs is easy to debug and maintain.
- Design Benefits : OOPs needs extensive design planning which certainly provide design benefits over traditional style.
For simple programming tasks, use of procedural programming style is well suited but as the program becomes complex and software architecture becomes large, object oriented programming is suitable to create modular designs and patterns. This makes it particularly useful when you create larger programs.
There are four major benefits to object-oriented programming:
- Encapsulation: in OOP, you bundle code into a single unit where you can determine the scope of each piece of data.
- Abstraction: by using classes, you are able to generalize your object types, simplifying your program.
- Inheritance: because a class can inherit attributes and behaviors from another class, you are able to reuse more code.
- Polymorphism: one class can be used to create many objects, all from the same flexible piece of code.
Languages evaluation criteria
https://www.cs.scranton.edu/~mccloske/courses/cmps344/sebesta_chap1.html
| Readability | Writability | Reliability | Cost | Other criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
This refers to the ease with which programs (in the language under consideration) can be understood. This is especially important for software maintenance.
|
This is a measure of how easily a language can be used to develop programs for a chosen problem domain.
|
This is the property of performing to specifications under all conditions.
|
The following contribute to the cost of using a particular language:
|
|
Imperative versus declarative code
Imperative paradigm
Procedural and object-oriented programming belong under imperative paradigm that you know from languages like C, C++, C#, PHP, Java and of course Assembly.
Your code focuses on creating statements that change program states by creating algorithms that tell the computer how to do things. It closely relates to how hardware works. Typically your code will make use of conditinal statements, loops and class inheritence.
Example of imperative code in JavaScript is:
class Number {
constructor (number = 0) {
this.number = number;
}
add (x) {
this.number = this.number + x;
}
}
const myNumber = new Number (5);
myNumber.add (3);
console.log (myNumber.number); // 8
Declarative paradigm
Logic, functional and domain-specific languages belong under declarative paradigms and they are not always Turing-complete (they are not always universal programming languages). Examples would be HTML, XML, CSS, SQL, Prolog, Haskell, F# and Lisp.
Declarative code focuses on building logic of software without actually describing its flow. You are saying what without adding how. For example with HTML you use
Example of declarative code in JavaScript is:
const sum = a => b => a + b;
console.log (sum (5) (3)); // 8
Names - Variables
A name is a string of characters used to identify some entity in a program. Variable names are the most common names in the programs.
- Are names case sensitive?
- Length?
- etc...
Names with special characters:
PHP: All variable names must begin with dollar signsPerl: All variable names begin with special characters, which specify the variable's typeRuby: Variable names that begin with@are instance variables; those that begin with@@are class variables
Case sensitivity names:
- Names in the
C-basedlanguages are case sensitive. Not in others languages.
Variables
A variable is an abstraction of a memory cell.
Variables can be characterized as a sextuplet (six parts) of attributes:
- Name
- Address
- Value
- Type
- Lifetime
- Scope
Address: The memory address with which it is associated.
- A variable may have different addresses at different times during execution.
- A variable may have different addresses at different places in a program.
- If two variable names can be used to access the same memory location, they are called aliases.
- Aliases are created via pointers, reference variables,
CandC++unions - Two pointer variables are aliases when they point to the same memory location. The same is true for reference variables.
- Aliases are harmful to readability (program readers must remember all of them).
Type: Determines the range of values of variables and the set of operations that are defined for values of that type; in the case of floating point, type also determines the precision
For example, the int type in Java specifies a value range of -2147483648 to 2147483647
Value: The value of a variable is the contents of the memory cell or cells associated with the variable:
- The l-value of a variable is its address
- The r-value of a variable is its value
Binding
A binding is an association between an entity and an attribute, such as between a variable and its type or value, or between an operation and a symbol.
Binding time is the time at which a binding takes place. Bindings can take place at:
- Language design time
- Language implementation time
- Compile time
- Load time
- Link time
- Run time
For example:
- The asterisk symbol (*) is usually bound to the multiplication operation at language design time. At compile time, a variable in a Java program is bound to a particular data type.
- Language design time: Bind operator symbols to operations
- Language implementation time: Bind floating point type to a representation
- Compile time: Bind a variable to a type in
CorJava - Load time: Bind a
CorC++static variableto a memory cell - Runtime: Bind a
nonstatic local variableto a memory cell
Static vs Dynamic Binding
https://techdifferences.com/difference-between-static-and-dynamic-binding.html
A binding is static if it first occurs before run time and remains unchanged throughout program execution.
A binding is dynamic if it first occurs during execution or can change during execution of the program.
Static vs Dynamic Binding in Java
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/static-vs-dynamic-binding-in-java/
Static Binding:
The binding which can be resolved at compile time by compiler is known as static or early binding. Binding of all the static, private and final methods is done at compile-time .
Why binding of static, final and private methods is always a static binding?Static binding is better performance wise (no extra overhead is required). Compiler knows that all such methods cannot be overridden and will always be accessed by object of local class. Hence compiler doesn’t have any difficulty to determine object of class (local class for sure). That’s the reason binding for such methods is static. Let’s see by an example:
public class NewClass { public static class superclass { static void print() { System.out.println("print in superclass."); } } public static class subclass extends superclass { static void print() { System.out.println("print in subclass."); } } public static void main(String[] args) { superclass A = new superclass(); superclass B = new subclass(); A.print(); B.print(); } }Output:
print in superclass. print in superclass.As you can see, in both cases print method of
superclassis called. Lets see how this happens:
- We have created one object of
subclassand one object ofsuperclasswith the reference of thesuperclass.- Since the
superclassisstatic, compiler knows that it will not be overridden insubclassesand hence compiler knows during compile time which print method to call and hence no ambiguity.As an exercise, reader can change the reference of object B to subclass and then check the output.
Dynamic Binding:
In Dynamic binding compiler doesn’t decide the method to be called. Overriding is a perfect example of dynamic binding. In overriding both parent and child classes have same method . Let’s see by an example:
public class NewClass { public static class superclass { void print() { System.out.println("print in superclass."); } } public static class subclass extends superclass { @Override void print() { System.out.println("print in subclass."); } } public static void main(String[] args) { superclass A = new superclass(); superclass B = new subclass(); A.print(); B.print(); } }Output:
print in superclass. print in subclass.
Here the output differs. But why? Let’s break down the code and understand it thoroughly:
- Methods are not static in this code.
- During compilation, the compiler has no idea as to which
runtimeand therefore the corresponding version of print will be called based on type on object.
Important points
- Private, final and static members (methods and variables) use static binding while for virtual methods (In Java methods are virtual by default) binding is done during run time based upon run time object.
- Static binding uses Type information for binding while Dynamic binding uses Objects to resolve binding.
- Overloaded methods are resolved (deciding which method to be called when there are multiple methods with same name) using static binding while overridden methods using dynamic binding, i.e, at run time.
Statically and Dynamically typed languages
Statically typed languages:
A language is statically typed if the type of a variable is known at compile time. For some languages this means that you as the programmer must specify what type each variable is (e.g.: Java, C, C++); other languages offer some form of type inference, the capability of the type system to deduce the type of a variable (e.g.: OCaml, Haskell, Scala, Kotlin)
The main advantage here is that all kinds of checking can be done by the compiler, and therefore a lot of trivial bugs are caught at a very early stage.
Examples: C, C++, Java, Rust, Go, Scala
Dynamically typed languages:
A language is dynamically typed if the type is associated with run-time values, and not named variables/fields/etc. This means that you as a programmer can write a little quicker because you do not have to specify types every time (unless using a statically-typed language with type inference).
Examples: Perl, Ruby, Python, PHP, JavaScript
Most scripting languages have this feature as there is no compiler to do static type-checking anyway, but you may find yourself searching for a bug that is due to the interpreter misinterpreting the type of a variable. Luckily, scripts tend to be small so bugs have not so many places to hide.
Most dynamically typed languages do allow you to provide type information, but do not require it. One language that is currently being developed, Rascal, takes a hybrid approach allowing dynamic typing within functions but enforcing static typing for the function signature.
Data type
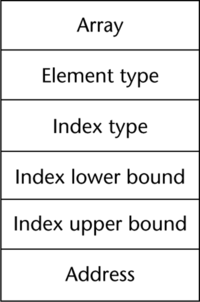
A data type, in programming, is a classification that specifies which type of value a variable has and what type of mathematical, relational or logical operations can be applied to it without causing an error. A string, for example, is a data type that is used to classify text and an integer is a data type used to classify whole numbers.
Descriptor:
It's the collection of the attributes of a variable.
Ex.:
| Example | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Primitive Data Types
|
Integer | byte
|
||
short
|
||||
int
|
||||
long
|
||||
| Floating Point | float
|
|||
double
|
||||
| Complex | Each value consists of two floats, the real part and the imaginary part | |||
| Boolean | ||||
| Character |
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
| Arrays | An array is a homogeneous aggregate of data elements in which an individual element is identified by its position in the aggregate, relative to the first element.
|
Slicing in Python: Python
vector = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16]
mat = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
vector (3:6) is a three-element array
mat[0][0:2] is the first and second element of the first row of mat
| ||
| Associative Arrays | An associative array is an unordered collection of data elements that are indexed by an equal number of values called keys:
Ex: Python: C++: Perl: |
Associative Arrays in Perl# Names begin with %; literals are delimited by parentheses
%hi_temps = ("Mon" => 77, "Tue" => 79, "Wed" => 65, ...);
# Subscripting is done using braces and keys
$hi_temps{"Wed"} = 83;
# Elements can be removed with delete
delete $hi_temps{"Tue"};
| ||
| Record | A record is a possibly heterogeneous aggregate of data elements in which the individual elements are identified by names | |||
| Enumeration | All possible values, which are named constants, are provided in the definition.
No enumeration variable can be assigned a value outside its defined range |
C# example:enum days {mon, tue, wed, thu, fri, sat, sun};
| ||
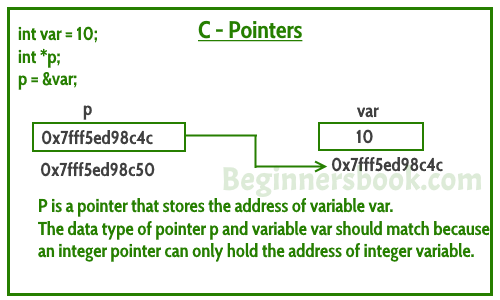
Pointer
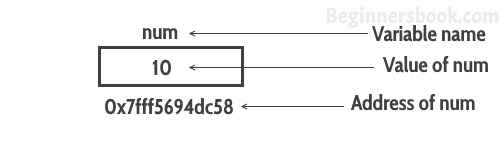
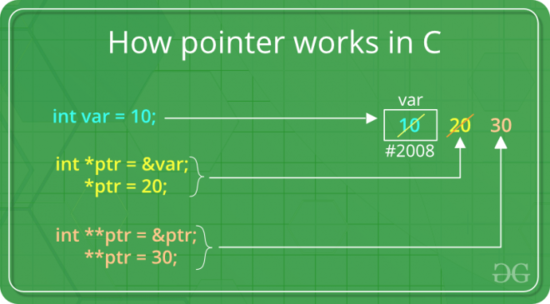
Pointers store address of variables or a memory location.
A pointer is a variable that stores the address of another variable. Unlike other variables that hold values of a certain type, pointer holds the address of a variable. For example, an integer variable holds (or you can say stores) an integer value, however an integer pointer holds the address of a integer variable. https://beginnersbook.com/2014/01/c-pointers/
- A pointer type variable has a range of values that consists of memory addresses and a special value, nil.
- Provide the power of indirect addressing
- Provide a way to manage dynamic memory
- A pointer can be used to access a location in the area where storage is dynamically created (usually called a heap)
Pointers in C and CPP
To use pointers in C, we must understand below two operators: & and *
| |||
|
Ampersand ( |
The unary operator For example |
// The output of this program can be different in different runs.
// Note that The program prints address of a variable and a variable
// can be assigned different address in different runs.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x = 10;
// Prints address of x
printf("%p", &x);
return 0;
}
|
|
|
Unary (Asterisk) ( |
To declare a pointer variable:
|
// C program to demonstrate declaration of
// pointer variables.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x = 10;
// 1) Since there is * in declaration, ptr becomes a pointer
// varaible (a variable that stores address of another variable)
// 2) Since there is int before *, ptr is pointer to an integer
// type variable
int *ptr;
// & operator before x is used to get address of x.
// The address of x is assigned to ptr.
ptr = &x;
return 0;
}
| |
|
To access the value stored in the address.
|
// C program to demonstrate use of * for pointers in C
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// A normal integer variable
int x = 10;
// A pointer variable that holds address of var.
int *ptr = &x;
// This line prints the value at the address stored in ptr.
// The Value stored is the value of variable "x"
printf("Value of x = %d\n", *ptr);
// The output of this line may be different in different
// runs even on the same machine.
printf("Address of x = %p\n", ptr);
// We can also use ptr as lvalue (Left hand side of assignment)
*ptr = 20; // Value at address is now 20
// This prints 20
printf("After doing *ptr = 20, *ptr is %d\n", *ptr);
return 0;
}
|
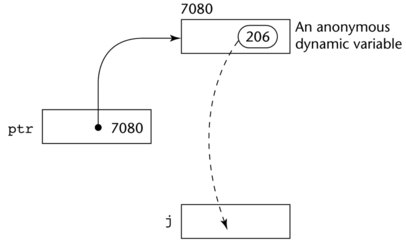
j = *ptr
| |
Object-Oriented Paradigm
Abstraction
https://stackify.com/oop-concept-abstraction/
Abstraction is a key concept in programming. In particular, it is one of the 4 fundamental concepts of object-oriented programming (OOP) languages. Its main goal is to handle complexity by hiding unnecessary details from the user. That enables the user to implement more complex logic on top of the provided abstraction without understanding or even thinking about all the hidden complexity.
Abstraction in the real world
I'm a coffee addict. So, when I wake up in the morning, I go into my kitchen, switch on the coffee machine and make coffee. Sounds familiar?
Making coffee with a coffee machine is a good example of abstraction:
- You need to know how to use your coffee machine to make coffee.
- You need to provide water and coffee beans,
- Switch the machine on,
- Select the kind of coffee you want to get ...
- The thing you don't need to know is how the coffee machine is working internally to brew a fresh cup of delicious coffee:
- You don't need to know how the coffee machine heat the water,
- You don't need to know the ideal temperature of the water,
- Neither the amount of ground coffee you need to use.
Someone else worried about all these details and created a coffee machine that now acts as an abstraction of the coffee making process and hides all these details. You just interact with a simple interface that doesn't require any knowledge about the internal implementation.
We can use the same concept in programming and specially in object-oriented programming languages...
Another good example of abstraction, is any Software or Application. Let's consider an Email Service Application (Gmail, for example)...
Abstraction in Programming
Abstraction is a concept much more easier than it seams to be. Every time that we create a
Functionor anObject, we are probably implementing abstraction. If thisFunctionorObjectcan be re-used in another part of the code or even in another program to perform a particular task, ourFunctionorObjectwill be acting as an abstraction of the task that is performing; just like the coffee machine of our previous example acts as an abstraction of the coffee making process by hiding all the complex details.
Two fundamental abstraction facilities:
- Process abstraction:
- Nearly all programming languages support process abstraction with subprograms (functions, for example)
- Data abstraction:
- Nearly all programming languages designed since 1980 support data abstraction (objects).
Abstraction in OOP
Objects in an OOP language provide an abstraction that hides the internal implementation details. Similar to the coffee machine in your kitchen, you just need to know which methods of the object are available to call and which input parameters are needed to trigger a specific operation. But you don't need to understand how this method is implemented and which kinds of actions it has to perform to create the expected result.
Let's implement the coffee machine example in Java. You do the same in any other object-oriented programming language. The syntax might be a little bit different, but the general concept is the same.
Abstract methods and classes in Java
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/IandI/abstract.html
An abstract class is a class that is declared abstract—it may or may not include abstract methods. Abstract classes cannot be instantiated, but they can be subclassed.
An abstract method is a method that is declared without an implementation (without braces, and followed by a semicolon), like this:
abstract void moveTo(double deltaX, double deltaY);
If a class includes abstract methods, then the class itself must be declared abstract, as in:
public abstract class GraphicObject { // declare fields // declare nonabstract methods abstract void draw(); }When an abstract class is subclassed, the subclass usually provides implementations for all of the abstract methods in its parent class. However, if it does not, then the subclass must also be declared abstract.
Interfaces in Java
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/IandI/createinterface.html
Abstract Classes Compared to Interfaces
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/IandI/abstract.html
Abstraction code example - Use abstraction to implement a coffee machine
Inheritance
Inheritance can be defined as the process where one class acquires the properties and behavior (methods and fields) of another class.
Inheritance enables code reusability as well as adding new features to the existing code.
- superclass (base class, parent class): The class whose properties are inherited.
- subclass (derived class, child class): The class which inherits the properties of other.
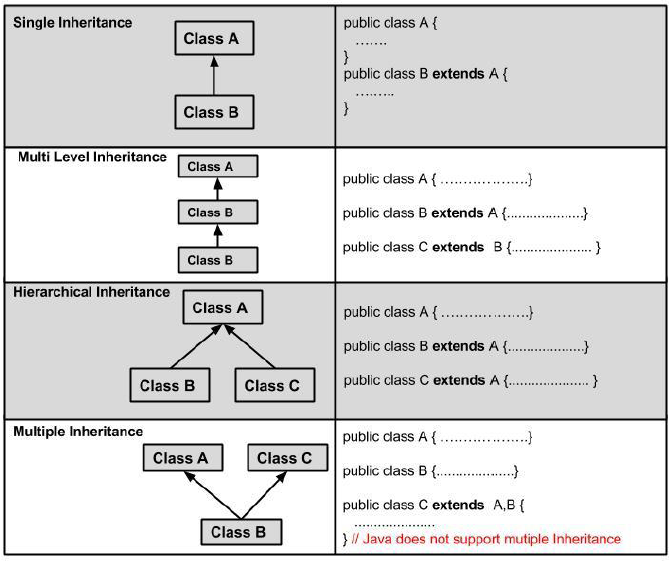
Types of inheritance
Single inheritance enables a derived class to inherit properties and behavior from only a single parent class.
Multiple inheritance enables a class can inherit characteristics and features from more than one parent class.
A very important fact to remember is that Java does not support multiple inheritance. This means that a class cannot extend more than one class. Therefore following is illegal:
public class extends Animal, Mammal{} // Illegal in Java
However, a class can implement one or more interfaces. This has made Java get rid of the impossibility of multiple inheritance.
Inheritance in Java
Extends keyword
extends is the keyword used to inherit the properties of a class. With use of the extends keyword the subclasses will be able to inherit all the properties of the superclass except for the private properties of the superclass.
Example:
class Super{
...
...
}
class Sub extends Super{
...
...
}
Calculation.java
package calculation;
class Calculation {
int z;
public void addition(int x, int y){
z=x+y;
System.out.println("The sum of the given numbers:"+z);
}
public void substraction(int x,int y){
z=x-y;
System.out.println("The difference between the given numbers:"+z);
}
}
MyCalculation.java
package calculation;
public class MyCalculation extends Calculation{
public void multiplication(int x, int y){
z = x*y;
System.out.println("The product of the given numbers is: "+z);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
int a=20, b=10;
MyCalculation demo = new MyCalculation();
demo.addition(a,b);
demo.substraction(a, b);
demo.multiplication(a, b);
}
}
Using extends keyword, My_Calculation inherits the methods addition() and Subtraction() from Calculation class.
You can instantiate the class as given below as well. But using the superclass reference variable ( cal in this case ) you cannot call the method multiplication(), which belongs to the subclass My_Calculation:
Calculation cal = new My_Calculation();
demo.addition(a, b);
demo.Subtraction(a, b);
A subclass inherits all the members (fields, methods, and nested classes) from its superclass. Constructors are not members, so they are not inherited by subclasses, but the constructor of the superclass can be invoked from the subclass.
The super keyword
The super keyword is similar to this keyword. The following are the scenarios where the super keyword is used.
- It is used to differentiate the members of superclass from the members of subclass, if they have same names.
- It is used to invoke the superclass constructor from subclass.
Differentiating the members
If a class is inheriting the properties of another class, and if the members of the superclass have the same names as the sub class, to differentiate these variables we use super keyword as shown below.
super.variable
super.method();
Sample Code
In the given program you have two classes namely Sub_class and Super_class, both have a method named display() with different implementations, and a variable named num with different values.
package btest2_the_super_keyword;
class Super_class{
int num=20;
//display method of superclass
public void display(){
System.out.println("This is the display method of superclass");
}
}
package btest2_the_super_keyword;
public class Sub_class extends Super_class {
int num=10;
//display method of sub class
public void display(){
System.out.println("This is the display method of subclass");
}
public void my_method(){
//Instantiating subclass
Sub_class sub=new Sub_class();
//Invoking the display() method of sub class
sub.display();
//Invoking the display() method of superclass
super.display();
//printing the value of variable num of subclass
System.out.println("value of the variable named num in sub class:"+ sub.num);
//printing the value of variable num of superclass
System.out.println("value of the variable named num in super class:"+ super.num);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Sub_class obj = new Sub_class();
obj.my_method();
}
}
Invoking Superclass constructor
If a class is inheriting the properties of another class, the subclass automatically acquires the default constructor of the super class. But if you want to call a parameterized constructor of the super class, you need to use the super keyword as shown below.
super(values);
class SuperClass{
int age;
SuperClass(int age){
this.age=age;
}
public void getAge(){
System.out.println("The value of the variable named age in super class is: " +age);
}
}
public class SubClass extends SuperClass {
SubClass(int age){
super(age);
}
public static void main(String argd[]){
SubClass s = new SubClass(24);
s.getAge();
}
}
Overriding
https://www.techopedia.com/definition/24010/overriding
Overriding is an object-oriented programming feature that enables a child class to provide different implementation for a method that is already defined and/or implemented in its parent class or one of its parent classes. The overriden method in the child class should have the same name, signature, and parameters as the one in its parent class.
Overriding enables handling different data types through a uniform interface. Hence, a generic method could be defined in the parent class, while each child class provides its specific implementation for this method.
C++ Inheritance
https://www.w3schools.com/cpp/cpp_inheritance.asp
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/cplusplus/cpp_interfaces.htm
Reflection
http://tutorials.jenkov.com/java-reflection/index.html#java-reflection-example
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/reflect/index.html
A programming language that supports reflection allows its programs to have runtime access to their types and structure and to be able to dynamically modify their behavior.
- The types and structure of a program are called
metadata
- The process of a program examining its metadata is called
introspection
- Interceding in the execution of a program is called
intercession
Java Reflection makes it possible to inspect classes, interfaces, fields and methods at runtime, without knowing the names of the classes, methods etc. at compile time. It is also possible to instantiate new objects, invoke methods and get/set field values using reflection. http://tutorials.jenkov.com/java-reflection/index.html#java-reflection-example
Uses of reflection for software tools:
- Class browsers need to enumerate the classes of a program
- Visual IDEs use type information to assist the developer in building type correct code
- Debuggers need to examine private fields and methods of classes
- Test systems need to know all of the methods of a class
Downsides of Reflection:
- Performance costs
- Exposes private fields and methods
- Voids the advantages of early type checking
- Some reflection code may not run under a security manager, making code non-portable
Reflection in Java
- Limited support from
java.lang.Class
- Java runtime instantiates an instance of
Classfor each object in the program
- The
getClassmethod ofClassreturns theClassobject of an object
float[] totals = new float[100];Class fltlist = totals.getClass();Class stg = "hello".getClass();
- If there is no object, use class field:
Class stg = String.class;
- Class has four useful methods:
getMethodsearches for a specific public method of a classgetMethodsreturns an array of all public methods of a classgetDeclaredMethodsearches for a specific method of a classgetDeclaredMethodsreturns an array of all methods of a class- The
Methodclass defines the invoke method, which is used to execute the method found bygetMethod
Here is a quick Java Reflection example to show you what using reflection looks like:
Method[] methods = MyObject.class.getMethods();
for(Method method : methods){
System.out.println("method = " + method.getName());
}
This example obtains the Class object from the class called MyObject. Using the class object the example gets a list of the methods in that class, iterates the methods and print out their names. http://tutorials.jenkov.com/java-reflection/index.html#java-reflection-example
Some tutorials
Examples from Introduction to Programming Using Python 3
http://www.cs.armstrong.edu/liang/py/ExampleByChapters.html
C++ tutorial
http://www.cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/program_structure/