Big Data Integration
Revision as of 22:11, 6 March 2019 by Adelo Vieira (talk | contribs)
Contents
Module Information
Module Objectives
- How to implement a cloud based storage solution for a company's big data needs
- The knowledge needed to integrate desktop and web applications to utilize web services and stored data.
- How cloud based DNS solutions can help to optimize a company's IT infrastructure
- How cloud based servers and service implementations can be easily deployed for rapid utilisation
- The steps involved in data exchange between web services and cloud based applications
Resources - References
- Programming Amazon EC2, Juirg van Vliet 1st 2011 O’Reilly
- Google Compute Engine, Marc Cohen 1st 2011 O’Reilly
- Python for Google App Engine, Massimiliano Pippi 1st 2015 Packet
- Big Data Fundamentals Concepts, Drivers & Techniques, Thomas Erl, Wajid Khattak, and Paul Buhler, Prentice Hall
Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA)
- A service-oriented architecture (SOA) is a style of software design where services are provided to the other components by application components, through a communication protocol over a network.
- A service is a discrete unit of functionality that can be accessed remotely and acted upon and updated independently, such as retrieving a credit card statement online.
- SOA provides access to reusable Web services over a TCP/IP network,
XML
Web service
- A software component stored on one computer that can be accessed via method calls by an application (or other software component) on another computer over a network
- Web services communicate using such technologies as:
- XML, JSON and HTTP
- Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP): An XML-based protocol that allows web services and clients to communicate in a platform-independent manner
Basic concepts:
- Remote machine or server: The computer on which a web service resides
- A client application that accesses a web service sends a method call over a network to the remote machine, which processes the call and returns a response over the network to the application
- Publishing (deploying) a web service: Making a web service available to receive client requests.
- Consuming a web service: Using a web service from a client application.
- In Java, a web service is implemented as a class that resides on a server.
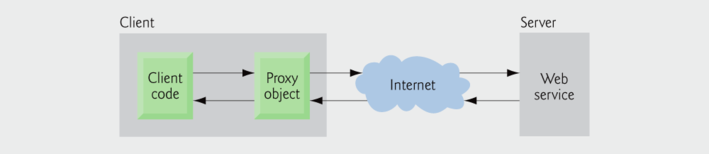
An application that consumes a web service (client) consists needs:
- An object of a proxy class for interacting with the web service.
- The proxy object handles the details of communicating with the web service on the client's behalf
JAX-WS:
- The Java API for XML Web Services (JAX-WS) is a Java programming language API for creating web services, particularly SOAP services. JAX-WS is one of the Java XML programming APIs. It is part of the Java EE platform.
- Requests to and responses from web services are typically transmitted via SOAP.
- Any client capable of generating and processing SOAP messages can interact with a web service, regardless of the language in which the web service is written.
Creating - Publishing - Testing and Describing a Web Service using NetBeans
- In Netbeans, you focus on the logic of the web service and let the IDE handle the web service’s infrastructure
- Example: HugeInteger web service:
- Provide methods that take two "huge integers" (represented as Strings)
- Can determine their sum, their difference, which is larger, which is smaller or whether the two numbers are equal
Create a Web Service - Locally
- We first need to to do some configuration in NetBeans:
- Go to /home/hduser/netbeans-8.2/etc/netbeans.conf:
- Find the line: netbeans_default_options
- If -J-Djavax.xml.accessExternalSchema=all is not between the quotes then paste it in.
- Go to /home/hduser/netbeans-8.2/etc/netbeans.conf:
- If you are deploying to the GlassFish Server you need to modify the configuration file of the GlassFish Server (domain.xml):
- /home/hduser/glassfish-4.1.1/glassfish/domains/domain1/config/domain.xml
- Find : <java-config
- Check the jvm-options for the following configuration
- <jvm-options>-Djavax.xml.accessExternalSchema=all</jvm-options>
- It should be there by default, if not paste it in, save file and exit
- You can now start Netbeans IDE
- /home/hduser/glassfish-4.1.1/glassfish/domains/domain1/config/domain.xml
- Create a Web Service in NetBeans:
- Choose File > New Project:
- Select Web Application from the Java Web category
- Change Project Name: to CalculatorWSApplication
- Set the server to GlassFish 4.1.1
- Set Java EE Version: Java EE 7 Web
- Set Context path: /CalculatorWSApplication
- After that you should now have a project created in the Projects view on the left hand side.
- Creating a WS from a Java Class:
- Right-click the CalculatorWSApplication node and choose New > Web Service.
- If the option is not there choose Other > Web Services > Web Service
- Click Next
- Name the web service CalculatorWS and type com.hduser.calculator in Package. Leave Create Web Service from Scratch selected.
- Select Implement Web Service as a Stateless Session Bean.
- Click Finish. The Projects window displays the structure of the new web service and the source code is shown in the editor area.
- Adding an Operation to the WS:
- Change to the Design view in the editor.
- Click the Add operation button.
- In the upper part of the Add Operation dialog box, type add in Name and type int in the Return Type drop-down list.
- In the lower part of the Add Operation dialog box, click Add and create a parameter of type int named num_1.
- Click Add again and create a parameter of type int called num_2.
- Click OK at the bottom of the panel to add the operation.
- Remove the default hello operation.
- Right click on hello operation and choose: Remove Operation
- Click on the source view to go back to view the code in the editor.
- You will see the default hello code is gone and the new add method is now there instead.
- Alter the code to now look like this.
- Well done, you have just created your first Web Service.
- To test the Web service drop down the Web Services directory and right click on CalculatorWSApplication.
- Choose Test Web service.
- Netbeans throws an error: It is letting us know that we have not deployed our Web Service.
- Right click on the main Project node and select deploy
- Testing the WS:
- Deploying the Web Service will automatically start the GlassFish server. Allow the server to start, this will take a little while. You can check the progress by clicking on the GlassFish tab at the bottom of the IDE.
- Wait until you see: «CalculatorWSApplication was successfully deployed in 9,912 milliseconds»
- Now you can right click on the Web Service as before and choose Test Web Service.
- The browser will open and you can now test the Web service and view the WSDL file.
Type 5 and 5 into the input fields and check that you get the response.
Consuming a Web Service in Java using NetBeans IDE
Netbeans 6.5 - 9 and Java EE enable programmers to "publish (deploy)" and/or "consume (client request)" web services
This document provides step-by-step instructions to consume a web service in Java using NetBeans IDE.
In the project, we will invoke a sorting web service through its WSDL link: http://vhost3.cs.rit.edu/SortServ/Service.svc?singleWsdl
- Step 1 - Createa JavaProject:
- We are going to name it: SortClient
- Step 2 - Generate a Web Service Client:
- After the Java Project has been created, go to the Project Tree Structure, Right click on Project and select New and then choose Web Service Client.
- Specify the WSDL URL as: http://vhost3.cs.rit.edu/SortServ/Service.svc?singleWsdl
- Click Finish
- Step 3 - Invoke the Service:
- Expand the Web Service References until you see the operation lists. Drag the operation you want to invoke to the source code window, such as "GetKey". A piece of code is automatically generated to invoke that operation.
- Drag MergeSort to the source code window and the corresponding code is automatically generated,too.
- In the main function, add the code to call the two functions: getKey() and mergeSort();As it is a call to a remote service, RemoteException needs to be listed in the throws cause