RapidMiner
RapidMiner is a data science software platform developed by the company of the same name that provides an integrated environment for data preparation, machine learning, deep learning, text mining, and predictive analytics. It is used for business and commercial applications as well as for research, education, training, rapid prototyping, and application development and supports all steps of the machine learning process including data preparation, results visualization, model validation and optimization. RapidMiner is developed on an open core model. The RapidMiner Studio Free Edition, which is limited to 1 logical processor and 10,000 data rows is available under the AGPL license. Commercial pricing starts at $2,500 and is available from the developer.
Contents
- 1 Installing RapidMiner
- 2 Training Videos
- 2.1 Introductions
- 2.2 Data Preparation AND ETL
- 2.3 Model and Validate
- 2.4 Operationalize
Installing RapidMiner
Descargamos el paquete y seguimos las instruciones en el sitio oficial: https://docs.rapidminer.com/latest/studio/installation/
./RapidMiner-Studio.sh
We will need to create a RapidMiner account.
Training Videos
https://rapidminer.com/training/videos/
En el ejemplo tratado en este training utilizamos una data que contiene cierta información de customers de una compañía cualquiera. Queremos hacer predicciones de los customers que son más propensos a suprimir su afiliación con la compañía. De esta forma, si sabemos cuales son los customer que probablemente suprimirán su afiliación, la compañía puede tomar las medidas necesarias to encourage them to stay as customers.
En este sentido, our data shows historical information about those customers that we know that have been «loyal» (leales) or «churners» (desleales). With this data we can built a model to make a prediction on the other customers that we don't know yet how they are likely to behave («loyal» or «churner»)
Introductions
https://rapidminer.com/training/videos/#introductions
Important terms: https://docs.rapidminer.com/latest/studio/getting-started/important-terms.html
GUI Intro
https://rapidminer.wistia.com/medias/dxnsrftr9i
The views
Design view
Work areas for specific taks...
Process panel: It is to dissing any process, like:
- Data loading
- Forecasting
- ...
- To get started with a very simple process we can place an operator into the process panel:
- For example, we can go to Data Access Operators and place (Drag and Drop) a «Retrieve» operator into the process panel.
- Luego de hacer esto y seleccionar (click) el operator en el Process panel, el Parameters Panel cambia y permitirá, a traveés del folder icon, seleccionar the file we want to load. Podemos, por ejemplo seleccionar la «Titanic data set» que se encuenra pre-loaded in RapidMiner-Studio.
- Then, in order to run the process, we need to connect the port of the «Retrieve» operator with the Result port.
- Then, to run the process we have to click the Run button (>) (or F11) y así RapidMiner ejecutará el proceso y automáticamente desplegará the Result View, where the data set is display by default as a table.
Ports:
Results view
Work areas for specific taks...
Auto Model view
Operators
Repository
- Through the repository panel you can access data and your process.
- Al iniciar un proyecto se recomienda crear un nuevo repositorio con dos sub-folders: data and processes
Parameters
Global Search
Adding extensions - The RapidMiner Marketplace
https://rapidminer.wistia.com/medias/9nu4i7b5ea
- To add extensions go to: Extensions > Marketplace:
- Top Downloads: some of the most popular extensions.
- Se recomienda instalar las siguientes:
- Text Processing
- Web Mining
- Python/R integration
- Anomaly Detection
- Series extension
- RapidMiner Radoop
- Luego de instalar la extension se the «Extension» folder in the «Operators» panel mostrará una nueva carpeta por cada extension instalada.
- También hay extension que adicionan una nueva «View». Por ejemplo, the «Radoop» extension adds the «Hadoop Data» view.
- To manage and uninstall extensions go to: Extensions > Manage Extensions
- Otra forma de instalar extensions es ir directamente al Marketplace website at: https://marketplace.rapidminer.com
- Descargamos el .jar file y lo colocamos en la «extension folder»: /home/adelo/.RapidMiner/extensions/
- Reiniciamos RapidMiner and the extension will become available.
Data Preparation AND ETL
https://rapidminer.com/training/videos/#data-preparation
Importing data
https://rapidminer.wistia.com/medias/t3b4v3hceb
The data used in this video is available here: http://docs.rapidminer.com/studio/getting-started/customer-churn-data.xlsx
- Iniciamos nuestro nuevo proyecto by creating a new repository with 2 sub-folders, let's call it:
- MyFirstPrediction
- data
- processes
- MyFirstPrediction
- Then, to import the data we can click the button «Import Data» and look for the file or we can just Drag and Drop the file into RapidMiner.
- In the second step (format your columns) we can change some of the properties of the attributes (columns):
- Change type: Real, Integer, etc
- Rename column
- Change Role: The default for each column is «General Attribute». We can change the role to: id, label, wight...
- In the second step (format your columns) we can change some of the properties of the attributes (columns):
Data loading via a process
https://rapidminer.wistia.com/medias/fyfagg7rp9
- Define the read operator we want:
- Go to the Operator panel and for this case we well use the «Read Excel» operator. So we Drag and Drop this operator into our Process panel.
- Go to the Parameters panel and click «Import configuration wizard»
- Look for the file
- After the file is load into the «Import configuration wizard» you can make the configuration you want:
- Change the role of the Churn Attribute to «Label».
- Connect the port to the result port.
- Hit the Run process button (>) (F11)
- Es muy importante notar la diferencia enter esté método para cargar la data y el anterior explciado en la sección Machine Learning#Importing data. La diferencia es que el presente método load the data into the RAN Memory; it doesn't store it into the local repository.
- Save the process into your local repository:
- File > Save process: then select the folder, or
- Go to the folder into the correct repository where you want to save the process: Right click > Store process here.
- Import/Export processes: That is only to save the process in another folder (export) and then import the process to our Process panel
- File > Import/Export process
- After you import a process, it will be into the process panel but not saved into your local repository. You can save it by right clicking the processes folder in your local repository > store process here.
- Delete a Repository:
- When you delete it from the Repository panel, you are just deleting the lick to it but not the files and folders inside it; if you want to delete them, you need to go to the file system and to it there (~/.RapidMiner/repositories).
- We can also save the data into our repository through the process adding a «Store» operator»:
- Drag and Drop the «Store operator» into the process panel (sobre la línea que conecta el the «Read Excel operator» y the result port).
- Then, in the Parameters panel click in the folder icon and indicate where you want to store the data.
- Then, hit the Run process button. That will store the data into the your local repository.
Visualizing data
https://rapidminer.wistia.com/medias/w623uxkoga
- Attribute = Column
- Regular attributes
- Special attributes:
- Label: Cuando una attributo es marcado como «Label» quiere decir que tal atributo es el que queremos que el modelo aprenda a predecir (It's the attribute that we want our model to learn to predict). So we are going to use the regular attributes to do so.
- Example = Row
- Example set = The entire data
- Data tab:
- When displaying data (in the Results View) we can sort the order of the attributes by clicking on the attribute (one click for ascending, a second click to descending and a third time to remove the sorting. By pressing the Ctrl key we can sort by multiple attributes.
- Statistics tab: RapidMiner do some automatic data discovery.
- We can display the data in different chart styles (Histogram, Scatter, Pie, etc).
- We can display multiple attributes in the same chart by clicking in the attributes shown in the «Plots box» using the Ctrl key.
- We can display the data in different chart styles (Histogram, Scatter, Pie, etc).
- To change the standard colors of the chart you can go to:
- Settings > Preferences:
- Color for minimum value in chart keys
- Color for maximum value in chart keys
- Settings > Preferences:
- Advanced charts tap:
- Example (using the «customer-churn-data»):
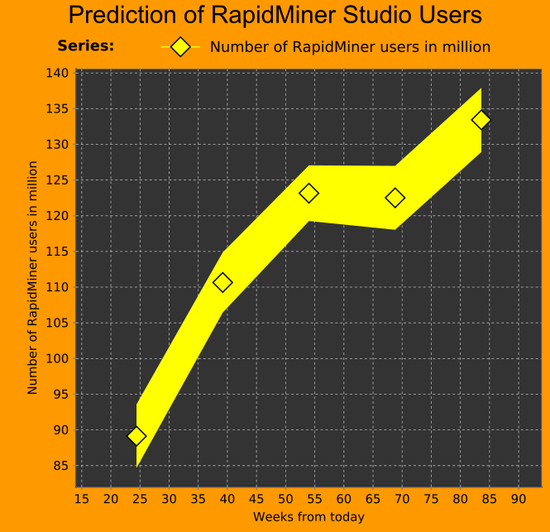
- Drag and Drop the «Age» attribute to the «Domain dimension» (that represent the x axis) and the «Last transaction» attribute to the «Empty axis» («Numerical axis) (that represent the y axis)
- Example (using the «customer-churn-data»):
- Having «Series: «LastTransaction» selected (clicking) from chart configuration box:
- Title: Number of RapidMiner users in million
- Visualization: Lines and shapes
- Some format configurations:
- Item shape: Diamond
- Color: Yellow
- Line stile: solid
- Aggregation: Average
- Indicators:
- Indicator type: Band
- Indicator 1: Drag and Drop age to this field.
- Indicator 2: Drag and Drop age to this field.
- Selecting Domain dimension from chart configuration box:
- Title: Weeks from today
- Selecting global configuration from chart configuration box:
- Chart title: Prediction of RapidMiner studio users
- Plot background: Change color to black
- Then you can export the plot:
- File > Print/Export Image
Turbo Prep
Introduction
https://rapidminer.wistia.com/medias/ar0409ddaw
Data Cleansing
https://rapidminer.wistia.com/medias/fui6gj5e8h
Merging Data
https://rapidminer.wistia.com/medias/1tdvusdi9q
Data Pivoting
Connecting to Databases
https://rapidminer.wistia.com/medias/th4jxcrww6
Data preparation
https://rapidminer.wistia.com/medias/p6kou5484b
- In reality data is never complete and without issues. Here we'll show you some of the operators that help to prepare and clean up the data.
- Loading the data:
- Let's start dragging and drop the «Read excel» operator into our process panel.
- Then, select the data panel via the parameters panel
- Connect the output port of the operator to the result port
- Run the process (> button or F11)
- Some of the problems the data can have are:
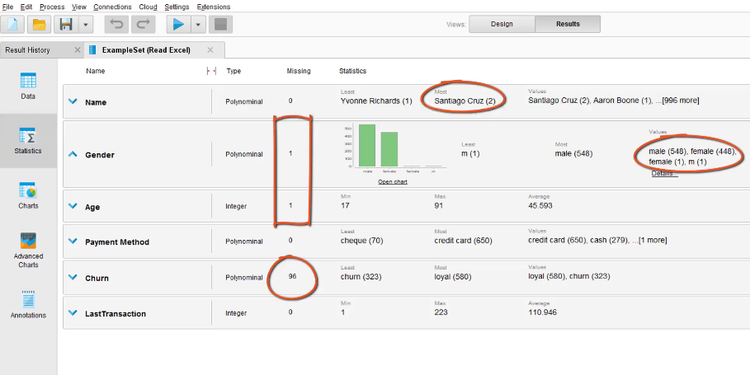
- White spaces in some rows. This can cause different problems. For example, in this data we have the attribute «Gender», that have 2 possible values: «male» or «female». So, if some of the rows have white spaces at the beginning or the end of the value (« femele») that will be interpreted as another value so we will have three values for the «Gender» attribute: «male», «female» and « female».
- Valores no definidos
- Repeated rows (duplicates)
- Para identificar problemas en la data debemos empezar mirando las estadíasticas de la data. Here we can see, for example:
- How many values are missing for each attribute.
- Duplicates.
- It is very important to notice that in our data we have customers that we know if they are «loyal» or «churners» and customers that we don't know yet how they are going to behave (so we don't have loyalty information for those ones). So the ones with «loyalty» information have to be placed in one subset to be used as input to create our model; and the customers without «loyalty» information are going to be grouped in another subset so we can predict how they will act.
White spaces
- To remove white spaces we use the «trim» operator:
Valores no definidos
Por ejemplo, en nuestra data tenemos algunas rows with missing «age» or «gender» values. Como en nuestra datas estos son sólo pocos, vamoa deshacernos de esas rows. Para esto:
- Agregamos el el operator «filter». al process panel.
- Para configurar dicho operator debemos hacer click en el «Add filter button» del parameters panel.
- En la ventana que se abrirá debemos elegir los atributos en los cuales queremos realizar cambios and set the filter to «Is not missing»
- Gender ---- Is not missing
- Age ---- Is not missing
Model and Validate
https://rapidminer.com/training/videos/#model-validate
Creating a Decision Tree Model
https://rapidminer.wistia.com/medias/foaj0o4si9
Applying the Model
https://rapidminer.wistia.com/medias/d4mfrw6bt0
Testing a Model
https://rapidminer.wistia.com/medias/imjv4717hu
Validating a Model
https://rapidminer.wistia.com/medias/qwsalih5st
Finding the right Model
https://rapidminer.wistia.com/medias/qmjo3wp59c
Optimization of the Model Parameters
https://rapidminer.wistia.com/medias/qie4nlf3in
Automate Model Selection and Optimization
https://rapidminer.wistia.com/medias/626q0hgcis
Auto Model
Operationalize
https://rapidminer.com/training/videos/#operationalize
Collaboration of RapidMiner Studio and Server
https://rapidminer.wistia.com/medias/yradsqx3nu
RapidMiner Server
Introduction to RapidMiner Server
https://rapidminer.wistia.com/medias/liyeu0vbmo
RapidMiner Server Installation
RapidMiner Server Installation - Preparations
https://rapidminer.wistia.com/medias/vv1za6naow