Difference between revisions of "Java Desktop App - Zoo Management System"
Adelo Vieira (talk | contribs) |
Adelo Vieira (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
} | } | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
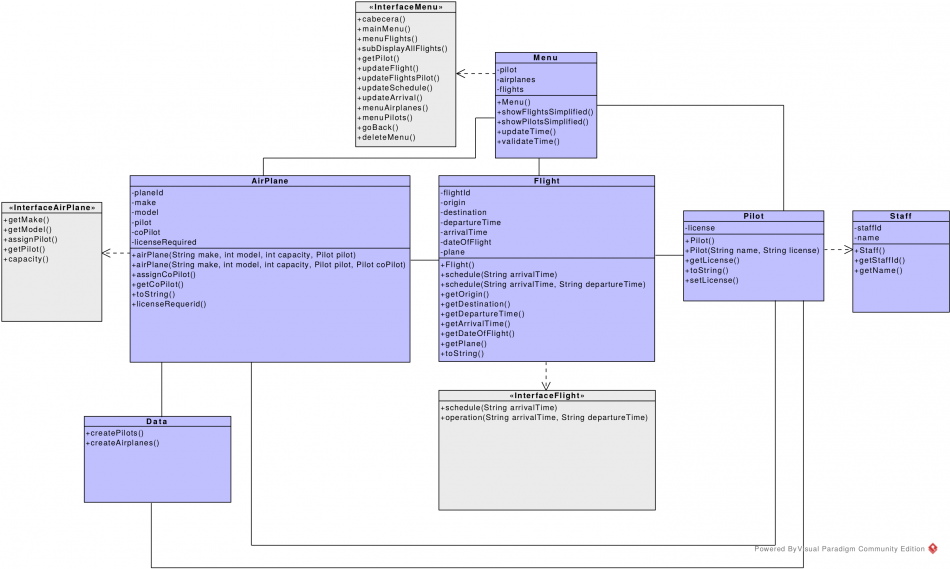
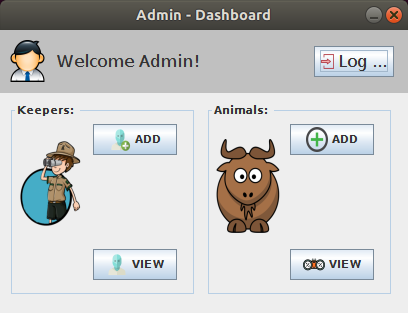
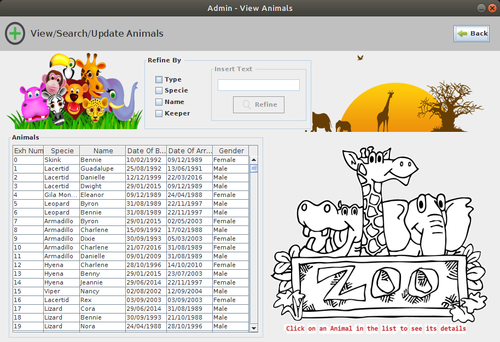
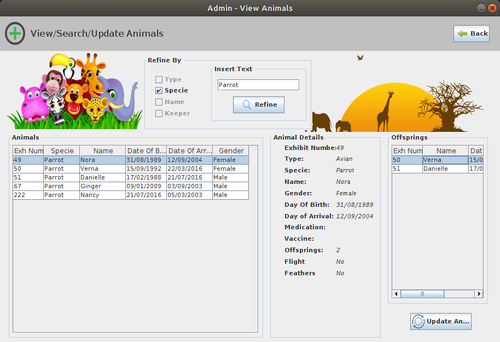
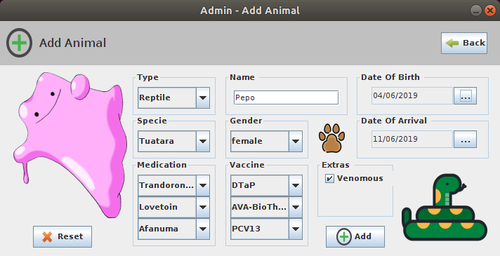
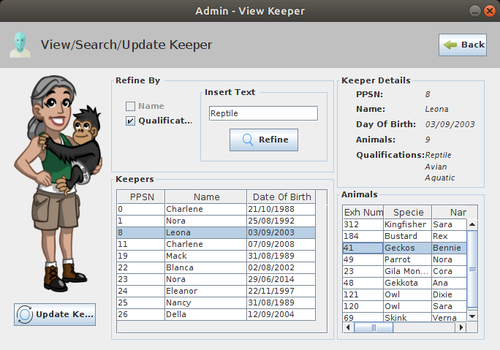
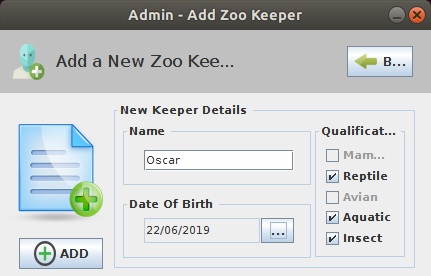
| + | ==Description of the GUI== | ||
| + | [[File:ZooManagementSystem_GUI_1.png|500px|thumb|center|]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ZooManagementSystem_GUI_2.png|500px|thumb|center|]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ZooManagementSystem_GUI_3.png|500px|thumb|center|]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ZooManagementSystem_GUI_4.png|500px|thumb|center|]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ZooManagementSystem_GUI_5.png|500px|thumb|center|]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ZooManagementSystem_GUI_6.png|500px|thumb|center|]] | ||
Revision as of 20:18, 22 June 2019
Contents
Project description
You have been tasked to create a Zoo management system.
- The Zoo has a number of Animals. These Animals are broken down into types:
- Mammal
- Reptile
- Avian
- Aquatic
- Insect
- Example Animals:
- Mammal:
- Tiger:
- date of birth, date of arrival, gender, ofspring, medicaton, vaccine, exhibit number
- Mammal:
- Avian
- Bat
- date of birth, date of arrival, fight, gender, ofspring, medication, vaccine, exhibit number
- Each Animal has a Zoo keeper that looks afer it:
- Zoo keepers are only allowed to care for animals if they are qualified to do so.
- A zoo keeper can look afer a max of 3 Animal types for a max of 10 animals.
- The system must allow a user to:
- Search for Animals.
- Search for Keepers.
- Add new animals.
- Add new keepers.
- Update animals.
- Update keepers.
- Your system must be run on test data before the Zoo will accept it:
- You are required to have a data set of at least 100 animals and 40 zoo keepers.
Requirements gathering and analysis
Classes diagram and reasoning behind the choices
Work plan and allocation of roles and responsibilities to each member of the development team
Ejemplo Código
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat c = new Cat();
System.out.println(c.health);
Dog d = new Dog();
System.out.println(d.health);
// // Upcasting
Mammal m = c; // Although there's no need to for programmer to upcast manually, it's legal to do so:
// Mammal m = (Mammal) new cat();
System.out.println(c); // This print: upcastingdowncasting.Cat@15db9742
System.out.println(m); // This will print the same: upcastingdowncasting.Cat@15db9742
// As you can see, Casting does not change the actual object type
// Cat is still exactly the same Cat after upcasting.
// It didn't change to a Mammal, it's just being labelled Mammal right now.
// This is allowed, because Cat is a Mammal.
// // Downcasting
if(m instanceof Cat){ // testing if the Animal is a Cat
System.out.println("It's a Cat! Now I can downcast it to a Cat, without a fear of failure.");
Cat c1 = (Cat)m; // Manual downcasting back to a Cat
}
// The following code will compile, but throws "java.lang.ClassCastException: Mammal cannot be cast to Cat" exception during runTime,
// because I’m trying to cast a Mammal, which is not a Cat, to a Cat.
Mammal m1 = new Mammal();
Cat c2 = (Cat)m1;
}
}
Description of the GUI