Difference between revisions of "Data Structures & Algorithms"
Adelo Vieira (talk | contribs) (→Array List) |
Adelo Vieira (talk | contribs) (→Single-Linked Lists) |
||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
==Single-Linked Lists== | ==Single-Linked Lists== | ||
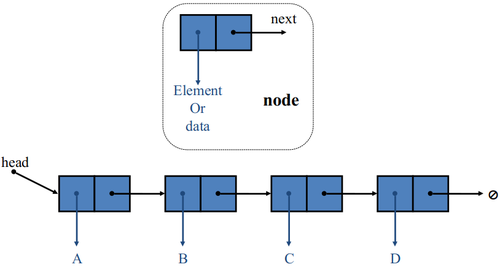
| + | * A singly linked list is a concrete data structure consisting of a sequence of nodes, starting from a head pointer. | ||
| + | * Each node stores | ||
| + | ** Element or data | ||
| + | ** Link (reference or address) to the next node | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Single_linked_lists.png|500px|thumb|center|]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * The ArrayList is limited because its add and remove methods operate in linear (O(n)) time—requiring a loop to shift elements. | ||
| + | * A linked list is useful for inserting and removing at arbitrary locations | ||
| + | ** In a linked list, instead of an index, each element is linked to the following element | ||
| + | ** A linked list can add and remove elements at a known location in O(1) time | ||
==Double-Linked Lists== | ==Double-Linked Lists== | ||
Revision as of 17:59, 14 October 2018
Array
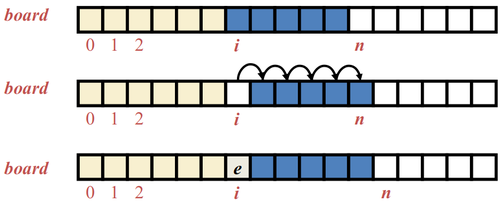
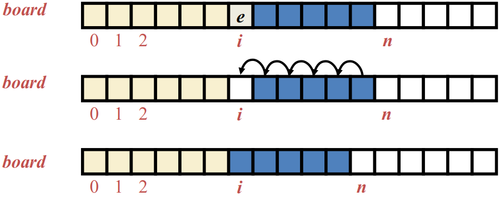
An array is a sequenced collection of variables all of the same type. Each variable, or cell, in an array has an index, which uniquely refers to the value stored in that cell. The cells of an array, A, are numbered 0, 1, 2, and so on. Each value stored in an array is often called an element of that array.
- An array can store primitive elements, such as characters.
- An array can also store references to objects.
- Adding an Entry:
- To add an entry e into array board at index i, we need to make room for it by shifting forward the n - i entries board[i],...,board[n - 1]
- Removing an Entry:
- To remove the entry e at index i, we need to fill the hole left by e by shifting backward the n - i - 1 elements board[i + 1],...,board[n - 1]
List ADT
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HdFG8L1sajw
List as Abstract Data Type. Cuando hablamos de ADT, queremos simplemente definir el comportamiento de la estructura de datos que queremmos; y no la definición estricta de una implementación en programación. Por tanto, en este sentido, a List ADT sería:
- A way to organize data
- Examples
- To-do list
- Gift lists
- Grocery Lists
- Examples
- Items in list have position
- Items may be added anywhere
- Write/modify items at a position.
Array Lists
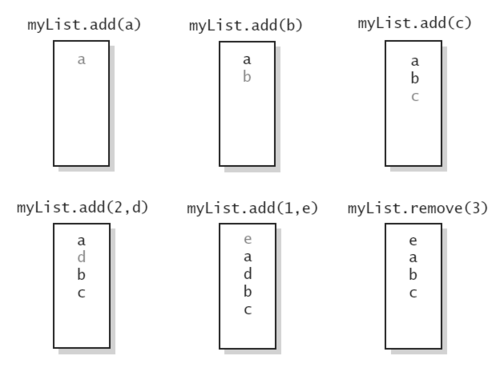
An obvious choice for implementing the list ADT is to use an array, A, where A[i] stores (a reference to) the element with index i. With a representation based on an array A, the get(i) and set(i, e) methods are easy to implement by accessing A[i] (assuming i is a legitimate index).
- Adding an Entry:
- As we already saw on Arrays, in an operation add(i,o), we need to make room for the new element by shifting forward the n - i elements A[i],..., A[n - 1]
- In the worst case (i = 0), this takes Order n time [O(n) times]
- In an add operation, when the array is full, instead of throwing an exception, we can replace the array with a larger one.
- Removing an Entry:
- In an operation remove(i), we need to fill the hole left by the removed element by shifting backward the n - i - 1 elements A[i + 1],..., A[n - 1]
- In the worst case (i = 0), this takes O(n) time
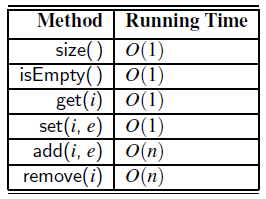
- Performance:
- In an array-based implementation of a dynamic list:
- The space used by the data structure is O(n)
- Indexing the element at i takes O(1) time
- add and remove run in O(n) time
- In an array-based implementation of a dynamic list:
Single-Linked Lists
- A singly linked list is a concrete data structure consisting of a sequence of nodes, starting from a head pointer.
- Each node stores
- Element or data
- Link (reference or address) to the next node
- The ArrayList is limited because its add and remove methods operate in linear (O(n)) time—requiring a loop to shift elements.
- A linked list is useful for inserting and removing at arbitrary locations
- In a linked list, instead of an index, each element is linked to the following element
- A linked list can add and remove elements at a known location in O(1) time