Difference between revisions of "Multi-Paradigm Programming and Scripting"
Adelo Vieira (talk | contribs) |
Adelo Vieira (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
A programming language that supports reflection allows its programs to have runtime access to their types and structure and to be able to dynamically modify their behavior | A programming language that supports reflection allows its programs to have runtime access to their types and structure and to be able to dynamically modify their behavior | ||
| − | The types and structure of a program are called <code>'''metadata'''</code> | + | * The types and structure of a program are called <code>'''metadata'''</code> |
| − | The process of a program examining its metadata is called <code>'''introspection'''</code> | + | * The process of a program examining its metadata is called <code>'''introspection'''</code> |
| − | Interceding in the execution of a program is called <code>'''intercession'''</code> | + | * Interceding in the execution of a program is called <code>'''intercession'''</code> |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Uses of reflection for software tools:''' | ||
| + | * Class browsers need to enumerate the classes of a program | ||
| + | * Visual IDEs use type information to assist the developer in building type correct code | ||
| + | * Debuggers need to examine private fields and methods of classes | ||
| + | * Test systems need to know all of the methods of a class | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | ===Reflection in Java=== | ||
| + | * Limited support from <code>java.lang.Class</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Java runtime instantiates an instance of <code>Class</code> for each object in the program | ||
| + | |||
| + | * The <code>getClass</code> method of <code>Class</code> returns the <code>Class</code> object of an object | ||
| + | :: <code>float[] totals = new float[100];</code> | ||
| + | :: <code>Class fltlist = totals.getClass();</code> | ||
| + | :: <code>Class stg = ″hello″.getClass();</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * If there is no object, use class field: | ||
| + | :: <code>Class stg = String.class;</code> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Revision as of 16:20, 30 October 2019
- Improved background for choosing appropriate languages
Contents
Compilation vs Interpretation
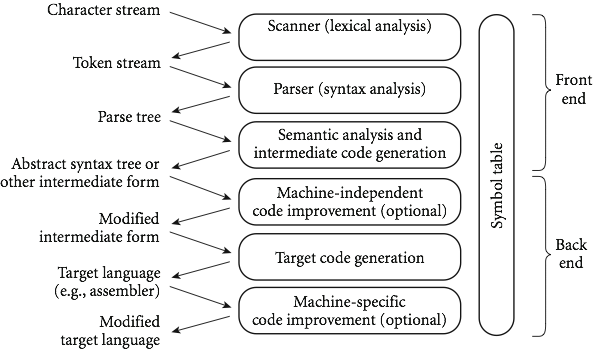
Phases of Compilation
C++ Inheritance
https://www.w3schools.com/cpp/cpp_inheritance.asp
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/cplusplus/cpp_interfaces.htm
Difference Between Static and Dynamic Binding
https://techdifferences.com/difference-between-static-and-dynamic-binding.html
Reflection in Java
A programming language that supports reflection allows its programs to have runtime access to their types and structure and to be able to dynamically modify their behavior
- The types and structure of a program are called
metadata
- The process of a program examining its metadata is called
introspection
- Interceding in the execution of a program is called
intercession
Uses of reflection for software tools:
- Class browsers need to enumerate the classes of a program
- Visual IDEs use type information to assist the developer in building type correct code
- Debuggers need to examine private fields and methods of classes
- Test systems need to know all of the methods of a class
Reflection in Java
- Limited support from
java.lang.Class
- Java runtime instantiates an instance of
Classfor each object in the program
- The
getClassmethod ofClassreturns theClassobject of an object
float[] totals = new float[100];Class fltlist = totals.getClass();Class stg = ″hello″.getClass();
- If there is no object, use class field:
Class stg = String.class;