Difference between revisions of "Cloud Computing"
Adelo Vieira (talk | contribs) (→Command-line interface for Google Cloud Platform (Cloud SDK)) |
Adelo Vieira (talk | contribs) (→Command-line interface for Google Cloud Platform (Cloud SDK)) |
||
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
The Cloud SDK is a set of tools for Cloud Platform. It contains [https://cloud.google.com/sdk/gcloud/reference/ '''gcloud'''], [https://cloud.google.com/storage/docs/gsutil '''gsutil'''], and [https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/docs/bq-command-line-tool '''bq'''], which you can use to access Google Compute Engine, Google Cloud Storage, Google BigQuery, and other products and services from the command-line. You can run these tools interactively or in your automated scripts. A comprehensive guide to gcloud can be found in [https://cloud.google.com/sdk/gcloud/ '''gcloud Overview''']. | The Cloud SDK is a set of tools for Cloud Platform. It contains [https://cloud.google.com/sdk/gcloud/reference/ '''gcloud'''], [https://cloud.google.com/storage/docs/gsutil '''gsutil'''], and [https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/docs/bq-command-line-tool '''bq'''], which you can use to access Google Compute Engine, Google Cloud Storage, Google BigQuery, and other products and services from the command-line. You can run these tools interactively or in your automated scripts. A comprehensive guide to gcloud can be found in [https://cloud.google.com/sdk/gcloud/ '''gcloud Overview''']. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Instalación==== | ||
| + | Para instalarlo, seguir el proceso de instalación mostrado en https://cloud.google.com/sdk/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Algunos comandos==== | ||
| + | To install or remove components at your current SDK version [197.0.0], run: | ||
| + | $ gcloud components install COMPONENT_ID | ||
| + | $ gcloud components remove COMPONENT_ID | ||
| + | |||
| + | To update your SDK installation to the latest version [197.0.0], run: | ||
| + | $ gcloud components update | ||
===Crear una Virtual Machine=== | ===Crear una Virtual Machine=== | ||
Revision as of 21:22, 14 April 2018
Vamos a trabajar con google cloud: https://console.cloud.google.com
Cloud computing refers to a utility-based provisioning of virtualized computa-tional resources over the Internet.
Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. This cloud model is composed of five essential characteristics, three service models, and four deployment models.
Contents
Essential Characteristics
On-demand self-service: A consumer can unilaterally provision computing capabilities, such as server time and network storage, as needed automatically without requiring human interaction with each service provider.
Broad network access: Capabilities are available over the network and accessed through standard mechanisms that promote use by heterogeneous thin or thick client platforms (e.g., mobile phones, tablets, laptops, and workstations).
Resource pooling: The provider's computing resources are pooled to serve multiple consumers using a multi-tenant model, with different physical and virtual resources dynamically assigned and reassigned according to consumer demand. There is a sense of location independence in that the customer generally has no control or knowledge over the exact location of the provided resources but may be able to specify location at a higher level of abstraction (e.g., country, state, or datacenter). Examples of resources include storage, processing, memory, and network bandwidth.
Rapid elasticity: Capabilities can be elastically provisioned and released, in some cases automatically, to scale rapidly outward and inward commensurate with demand. To the consumer, the capabilities available for provisioning often appear to be unlimited and can be appropriated in any quantity at any time.
Measured service: Cloud systems automatically control and optimize resource use by leveraging a metering capability1 at some level of abstraction appropriate to the type of service (e.g., storage, processing, bandwidth, and active user accounts). Resource usage can be monitored, controlled, and reported, providing transparency for both the provider and consumer of the utilized service.
On-Premise Computing:
- Requires hardware, space, electricity, cooling
- Requires managing OS, applications and updates
- Software Licensing
- Difficult to scale:
- Too much or too little capacity
- High upfront capital costs
- You have complete control
Cloud Computing:
- Shared, multi-tenant environment
- Pools of computing resources
- Resources can be requested as required
- Available via the Internet
- Private clouds can be available via private WAN
- Pay as you go
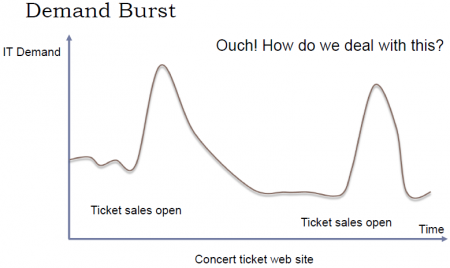
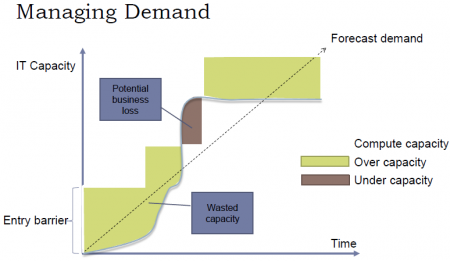
Una de las ventajas más importantes del Cloud es que puede ser «scaled» fácilmente (Resources can be requested as required). En otras palabras, a través del cloud la capacidad se puede variar fácilmente con respecto a la demanda. sólo cuando la demanda sea alta, el sistema será configurado para disponer de gran capacidad. On-Premise Computing, lo que generalmente pasa es que se configura el sistema para cubrir una capacidad promedio y generalmente se debe sobreestimar para que, cuando la demanda sea alta, poder todavía cubrirla. Entonces, cuando la demanda es baja estamos a "over capacity" y podría también pasar que cuando la demanda sea muy alta estemos a "under capacity". Esto es solucionado en el cloud. Esto se puede visualizar a través del ejemplo presentado en las siguientes figuras, en el cual se plantea el caso de un Concert ticket web site.
Service Models
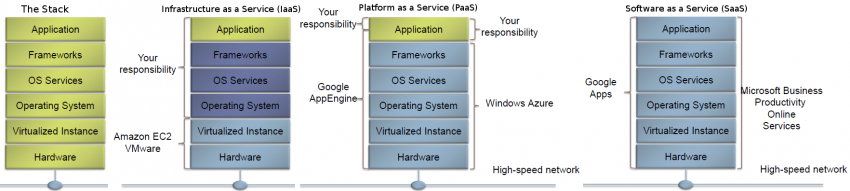
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) - Platform as a Service (PaaS) - Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS): The capability provided to the consumer is to use the provider’s applications running on a cloud infrastructure2. The applications are accessible from various client devices through either a thin client interface, such as a web browser (e.g., web-based email), or a program interface. The consumer does not manage or control the underlying cloud infrastructure including network, servers, operating systems, storage, or even individual application capabilities, with the possible exception of limited user-specific application configuration settings.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): The capability provided to the consumer is to deploy onto the cloud infrastructure consumer-created or acquired applications created using programming languages, libraries, services, and tools supported by the provider.3 The consumer does not manage or control the underlying cloud infrastructure including network, servers, operating systems, or storage, but has control over the deployed applications and possibly configuration settings for the application-hosting environment.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): The capability provided to the consumer is to provision processing, storage, networks, and other fundamental computing resources where the consumer is able to deploy and run arbitrary software, which can include operating systems and applications. The consumer does not manage or control the underlying cloud infrastructure but has control over operating systems, storage, and deployed applications; and possibly limited control of select networking components (e.g., host firewalls).
Deployment Models
Private cloud: The cloud infrastructure is provisioned for exclusive use by a single organization comprising multiple consumers (e.g., business units). It may be owned, managed, and operated by the organization, a third party, or some combination of them, and it may exist on or off premises.
Community cloud: The cloud infrastructure is provisioned for exclusive use by a specific community of consumers from organizations that have shared concerns (e.g., mission, security requirements, policy, and compliance considerations). It may be owned, managed, and operated by one or more of the organizations in the community, a third party, or some combination of them, and it may exist on or off premises.
Public cloud: The cloud infrastructure is provisioned for open use by the general public. It may be owned, managed, and operated by a business, academic, or government organization, or some combination of them. It exists on the premises of the cloud provider.
Hybrid cloud: The cloud infrastructure is a composition of two or more distinct cloud infrastructures (private, community, or public) that remain unique entities, but are bound together by standardized or proprietary technology that enables data and application portability (e.g., cloud bursting for load balancing between clouds).
Google Cloud Platform
https://console.cloud.google.com
Lo primero que tenemos que hacer es crear un proyecto. Generalmente hay un proyecto by default llamado «My First Project». Para crear un proyecto debemos ir a la pestaña que se encuentra justo al lado del Main Menu (Hamburger).
Command-line interface for Google Cloud Platform (Cloud SDK)
The Cloud SDK is a set of tools for Cloud Platform. It contains gcloud, gsutil, and bq, which you can use to access Google Compute Engine, Google Cloud Storage, Google BigQuery, and other products and services from the command-line. You can run these tools interactively or in your automated scripts. A comprehensive guide to gcloud can be found in gcloud Overview.
Instalación
Para instalarlo, seguir el proceso de instalación mostrado en https://cloud.google.com/sdk/
Algunos comandos
To install or remove components at your current SDK version [197.0.0], run:
$ gcloud components install COMPONENT_ID $ gcloud components remove COMPONENT_ID
To update your SDK installation to the latest version [197.0.0], run:
$ gcloud components update
Crear una Virtual Machine
Main Menu (Hamburger) > Compute Engine > VM instances:
- Create Instance
Crear storage
Main Menu > Storage > Browser:
- Create bucket
Luego de crearlo podemos copiar archivos al bucket. Hay diferentes formas de hacerlo:
- Sinple drag and drop
- Usando el terminal de Google cloud
- Desde el terminal de la computadora se puede hacer luego de instalar el programa Cloud SDK a través de:
- gsutil cp file.txt gs://adelobucket